How to Ship Frozen Food: Expert Tips for Chilled Delivery

Navigating the management of frozen food shipping can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and approach, it’s entirely manageable.
In this comprehensive guide on how to ship frozen food, we’ll examine the essential steps and best practices for ensuring your perishable goods reach their destination in optimal condition.
From selecting the appropriate packaging materials to mastering temperature control and choosing reliable shipping methods, we’ll equip you with the expertise needed to confidently ship frozen food, whether you’re a small business or an individual sending a thoughtful gift across the miles.
What are Frozen Foods?
Frozen foods are food items that have been subjected to freezing temperatures to preserve their freshness and extend their shelf life.
This process involves lowering the temperature of the food to below its freezing point, typically around 0°F (-18°C), to slow down the growth of bacteria, yeast, and mold that cause spoilage.
By freezing food, moisture within the product is converted into ice crystals, which helps to maintain its texture, flavor, and nutritional value over time.
Frozen foods encompass a wide range of products, including fruits, vegetables, meats, seafood, prepared meals, and desserts, making them convenient options for consumers seeking convenience without compromising quality.
Whether purchased from grocery stores or prepared at home and stored in a freezer, frozen foods provide a convenient and adaptable solution for meal planning and preserving perishable ingredients.
Why are Frozen Foods Used?
Before understanding how to ship frozen food you must know why they are used in the first place.
Frozen foods are utilized for various reasons, primarily for their convenience, extended shelf life, and preservation of nutrients. Here’s a breakdown:
- Convenience: Frozen foods offer quick and easy meal solutions. They eliminate the need for extensive preparation time since they are often pre-cooked or pre-cut. This is particularly beneficial for busy individuals or families with hectic schedules.
- Extended Shelf Life: Freezing effectively slows down the growth of microorganisms that cause food spoilage. This allows frozen foods to be stored longer without significantly deteriorating quality, taste, or nutritional value compared to fresh alternatives.
- Preservation of Nutrients: Properly frozen foods can retain their nutrients well. Flash-freezing techniques are often employed to preserve the nutritional content of fruits, vegetables, and meats. This means that even though frozen, they can still offer similar nutritional benefits as fresh produce.
- Year-Round Availability: Frozen foods provide access to seasonal items year-round. Fruits and vegetables can be picked and frozen at their peak ripeness, preserving flavour and nutrients. This allows consumers to enjoy a diverse range of produce regardless of the season.
- Reduced Food Waste: Frozen foods can help reduce food waste by allowing consumers to buy in bulk and store excess quantities for future use. This can be especially useful for items that may spoil quickly if not consumed promptly.
Frozen foods serve as convenient, nutritious, and efficient options for modern-day lifestyles, offering various choices to suit different dietary preferences and needs.
By following these steps, you can effectively ship frozen food while maintaining its quality and ensuring it reaches its destination in optimal condition.
Methods of Shipping Frozen Foods
Shipping frozen foods involves various methods to ensure they remain frozen and intact during transit. Here are some common methods:
- Dry Ice: Dry ice is a popular choice for shipping frozen foods because of its extremely low temperature (-78.5°C or -109.3°F). It transfers directly from a solid to a gas, creating a cooling effect that keeps the contents frozen. Dry ice is typically placed in insulated packaging with the frozen food to maintain the required temperature.
- Gel Packs or Ice Packs: Gel packs or ice packs are another option for maintaining cold temperatures during shipping. These packs are pre-frozen and can be placed alongside the frozen food to provide a cooling effect. Gel packs are reusable and can be refrozen for future use, making them a convenient and cost-effective solution.
- Insulated Packaging: Insulated packaging materials such as foam coolers, insulated boxes, or thermal bags help minimize heat transfer and maintain the cold temperature inside the package. These materials provide additional protection against external temperature fluctuations during transit.
- Expedited Shipping: Fast shipping services ensure that frozen food spends less time in transit, reducing the risk of thawing. Expedited shipping options include shipping carriers’ overnight or express delivery services, ensuring the frozen food reaches its destination quickly and safely.
- Temperature Monitoring: Some shipping methods incorporate temperature monitoring devices or data loggers to track the package’s temperature during transit. This allows shippers to ensure that the frozen food remains within the required temperature range throughout the shipping process.
- Specialized Carriers: Certain shipping carriers specialize in transporting perishable goods, including frozen foods. These carriers have the equipment and expertise to handle temperature-sensitive shipments and ensure they arrive at their destination in optimal condition.
By utilizing these methods, shippers can effectively transport frozen foods while maintaining their quality and ensuring they remain frozen until they reach their destination.
How to Ship Frozen Food
Shipping frozen food necessitates precise steps and adequate packaging to preserve its quality and ensure it reaches its destination still frozen.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to ship frozen food:
1. Choose the Right Carrier

When learning how to ship frozen food, choosing a carrier offering overnight or express shipping services is essential to minimize transit time.
Ensure they specialize in shipping perishable items and provide temperature-controlled options. Look for carriers with experience in handling frozen goods and a track record of reliability.
Consider factors such as the carrier’s coverage area, shipping rates, and customer reviews to make an informed decision.
Additionally, inquire about the carrier’s policies for handling perishable items and their procedures for addressing any issues that may arise during transit.
2. Select Suitable Packaging

Selecting suitable packaging is a critical step in the guide on how to ship frozen food.
The packaging must be robust enough to withstand handling during transit while effectively insulating the contents to maintain their frozen state.
Common materials for packaging frozen food shipments include insulated boxes or coolers with thermal insulation, such as foam or bubble wrap.
3. Prepare the Frozen Food

Once the frozen food products are selected and gathered, preparing them appropriately for shipping is crucial. This step involves carefully packaging the items to maintain their frozen state throughout transit.
Each item should be individually wrapped or placed in airtight containers to prevent freezer burn and preserve freshness.
Additionally, when considering how to ship frozen food, it’s important to use insulated packaging materials such as foam coolers or dry ice to create a cold environment within the shipping container.
Dry ice is particularly effective for maintaining low temperatures during transit but requires careful handling due to its extreme coldness.
4. Packaging Process
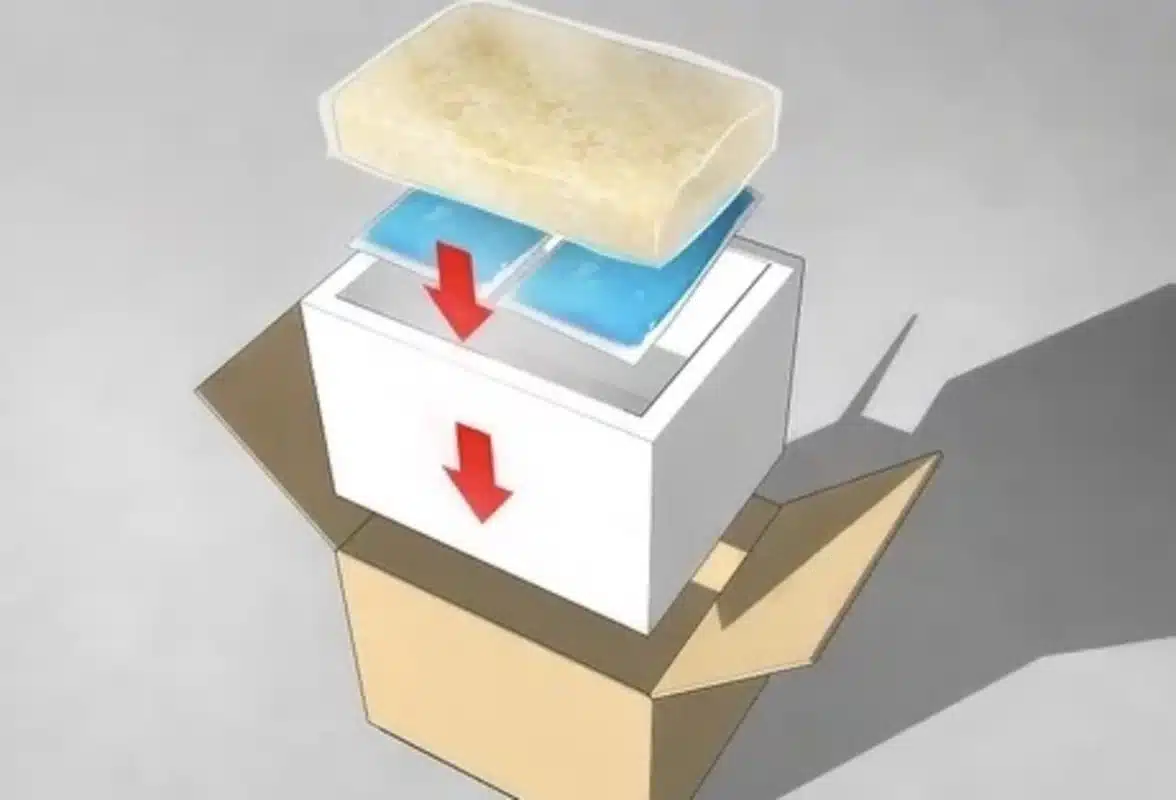
The packaging process is a critical step of the guide on how to ship frozen food, ensuring the preservation and quality of products during transit.
The first step involves selecting appropriate packaging materials designed to maintain low temperatures, such as insulated containers or boxes lined with thermal insulation.
These materials protect against external temperature changes, safeguarding the frozen items’ integrity.
Once the packaging materials are chosen, the next step involves carefully arranging the frozen food products within the containers.
Proper spacing and organization allow optimal airflow and temperature distribution, preventing hot spots or uneven freezing.
Techniques like layering with ice packs or dry ice can enhance cooling and prolong the frozen state during transit. After packing, containers are sealed to prevent leakage or exposure to external elements.
This may involve heat sealing, adhesive tapes, or other methods to create a tight seal and maintain the internal cold environment.
5. Labelling

Labeling is a crucial step in shipping frozen food. It ensures that packages are accurately identified and handled throughout their journey.
Each package must be clearly labelled with important information such as the contents, expiration date, handling instructions (such as “Keep Frozen“), and special handling requirements.
Labels should also include information about the shipment’s origin and destination and any necessary regulatory or safety labels.
Proper labeling helps ensure that the frozen food arrives safely and maintains its quality during transit, while also allowing for efficient sorting and handling by shipping personnel.
Additionally, clear and accurate labelling can help prevent delays, confusion, and potential issues with compliance or food safety regulations.
Therefore, attention to detail and sticking to labeling requirements are essential for successfully shipping frozen food products.
6. Shipping
When considering how to ship frozen food, the shipping step becomes essential in maintaining the integrity of perishable goods.
After carefully packing and labeling the frozen items, attention turns to the shipping process. Ensuring that the items remain at the correct temperature throughout transit is critical.
Various shipping methods, such as express services with refrigerated trucks or specialized cold storage containers, may be employed depending on distance and destination.
These methods help maintain temperatures below freezing, preventing melting and spoilage. Furthermore, using proper insulation and packaging materials adds extra protection during transportation.
Incorporating monitoring devices like temperature sensors allows for real-time tracking to ensure optimal conditions are upheld.
Choosing reputable shipping carriers experienced in handling frozen goods is essential for secure and timely delivery.
By following these careful shipping procedures, businesses can uphold the quality and safety of their frozen food products and meet customer expectations.
Final Thoughts
In wrapping up our guide on how to ship frozen food, it’s evident that the successful shipping of perishable goods depends on careful planning and execution.
By sticking to the outlined steps, which encompass proper packaging techniques, judicious selection of shipping methods, and collaboration with trusted carriers, businesses can ensure frozen products’ safe and reliable transportation.
Shipping frozen food can be challenging but certainly possible.
DevDiggers enables eCommerce businesses to ease their shipping processes from cart to doorstep by providing inventory management, order tracking, shipping label automation, and other features with premium WooCommerce extensions and development services.
FAQs
Can I use regular ice packs to ship frozen food?
While regular ice packs can help keep items cold, they may not be as effective as specialized gel packs or dry ice for extended shipping durations. Using gel packs specifically designed for frozen goods is recommended or consult with your shipping carrier for guidance on suitable cooling methods.
What should I do if my frozen food arrives melted?
If your frozen food arrives thawed, it’s essential to check the temperature of the items immediately. Discard any perishable items that have reached unsafe temperatures, and contact the shipping carrier or supplier to report the issue and seek a resolution or refund.
Are there any restrictions on shipping certain types of frozen food?
There may be restrictions on shipping certain types of frozen food, such as items that require special handling or have specific storage requirements. It’s important to familiarize yourself with applicable regulations and restrictions before shipping to avoid delays or issues with your shipment.
How long can frozen food stay frozen during shipping?
The duration of time that frozen food stays frozen during shipping depends on factors like insulation quality, outside temperature, and shipping method. Typically, with proper packaging and insulation, frozen food can remain frozen for 24 to 48 hours during transit.
Can I ship frozen food internationally?
Shipping frozen food internationally can be challenging due to customs regulations and varying transit times. To ensure compliance and assess additional requirements or restrictions, it’s best to check with the shipping carrier and the destination country’s import regulations.

Kartika Musle
A Tech enthusiast and skilled wordsmith. Explore the digital world with insightful content and unlock the latest in tech through my vision.

Leave a Reply