- Why WordPress Security Matters
- WordPress Security Checklist 2025: 25 Essential Ways
- 1. Keep WordPress Updated
- 2. Use Strong Passwords and Change Them Regularly
- 3. Limit Login Attempts
- 4. Install a Reputable Security Plugin
- 5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
- 6. Change the Default "Admin" Username
- 7. Use the Latest PHP Version
- 8. Secure the wp-config.php File
- 9. Use HTTPS With an SSL Certificate
- 10. Disable File Editing in the Dashboard
- 11. Regular Backups
- 12. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- 13. Set Correct File Permissions
- 14. Hide WordPress Version
- 15. Implement Security Headers
- 16. Remove Unused Themes and Plugins
- 17. Monitor and Audit Logs
- 18. Harden Your Database
- 19. Defend Against Bots and Spam
- 20. Implement Brute Force Prevention
- 21. Restrict Access to wp-admin
- 22. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) With Security Features
- 23. Disable PHP File Execution in Untrusted Directories
- 24. Disable Directory Indexing and Browsing
- 25. Set Up Automatic Logouts for Idle Users
- Final Thoughts on our WordPress Security Checklist
- Frequently Asked Questions: How to Improve WordPress Security
WordPress Security Checklist: 25 Methods to Protect Your Website

- Why WordPress Security Matters
- WordPress Security Checklist 2025: 25 Essential Ways
- 1. Keep WordPress Updated
- 2. Use Strong Passwords and Change Them Regularly
- 3. Limit Login Attempts
- 4. Install a Reputable Security Plugin
- 5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
- 6. Change the Default "Admin" Username
- 7. Use the Latest PHP Version
- 8. Secure the wp-config.php File
- 9. Use HTTPS With an SSL Certificate
- 10. Disable File Editing in the Dashboard
- 11. Regular Backups
- 12. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- 13. Set Correct File Permissions
- 14. Hide WordPress Version
- 15. Implement Security Headers
- 16. Remove Unused Themes and Plugins
- 17. Monitor and Audit Logs
- 18. Harden Your Database
- 19. Defend Against Bots and Spam
- 20. Implement Brute Force Prevention
- 21. Restrict Access to wp-admin
- 22. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) With Security Features
- 23. Disable PHP File Execution in Untrusted Directories
- 24. Disable Directory Indexing and Browsing
- 25. Set Up Automatic Logouts for Idle Users
- Final Thoughts on our WordPress Security Checklist
- Frequently Asked Questions: How to Improve WordPress Security
With over 40% share of internet usage, WordPress has become a lucrative target for cybercriminals and other hackers. Regardless if it’s a personal blog or a business website, WordPress security should never be ignored.
In this guide, we explain the WordPress security checklist for 2025 and go through each step so you do not have to deal with cyber-attacks. Continue reading to find out the ways you can defend your website, keep your private information safe, and strengthen your digital presence.
Starting off, you will find tips that, when followed, will improve your site’s security posture. Keeping your WordPress core updated is one of the most important practices that should be adhered to without fail.
Still, other steps like adding security headers, two-factor authentication, and more advanced steps are also necessary. We will discuss all in this article.
All steps taken into consideration will make sure you will secure WordPress and help you improve overall security.
Why WordPress Security Matters
Before we uncover the WordPress security checklist, it is crucial to grasp why the security of WordPress should be a concern.
- Massive Target: Due to its extensive use, WordPress makes up a big portion of cyber attacks. Even the slightest chance of a security hole can be abused for malicious purposes.
- Sensitive Information: Your site could have sensitive information ranging from customers to unpublished works. The loss of trust can lead to theft and tarnish your reputation.
- Search Engines: Websites that have been hacked are looked down upon by other platforms, such as Google, and are punished by losing their place in the rankings. Additionally, wordpress security issues are damaging for a company, so a loss in regard to reputation and consumer trust is also on the horizon.
- IT Security: When it comes to customer information, security is an issue for every business. It’s a matter of basic compliance, and adding a few rules like the GDPR makes it mandatory.
In light of these factors, insufficient applicable security measures will lead to disastrous consequences. WordPress and other platforms should embrace these solutions to secure themselves and explore 25 ways in this WordPress security checklist that could protect you against harm.
WordPress Security Checklist 2025: 25 Essential Ways
In a landscape of ever-evolving cyber threats, these 25 methods of our WordPress security checklist offer essential steps to strengthen your WordPress site’s defenses, reduce vulnerabilities, and secure your online presence.
1. Keep WordPress Updated
Why It Matters
WordPress frequently releases updates that not only add new features but also fix vulnerabilities. Hackers tend to exploit outdated installations. Keeping WordPress core, themes, and plugins updated is a fundamental step in protecting your website.
You can check your current WordPress version from the WordPress Dashboard.
How To Do It
- Regularly log in to your WordPress dashboard to check for updates.
- Enable automatic WordPress security updates where possible.
- Subscribe to official WordPress blogs or newsletters for timely notifications.
2. Use Strong Passwords and Change Them Regularly

Why It Matters
Outdated or reused passwords result in lower security, allowing attackers to infiltrate your site using brute force techniques. Implementing strong and unique passwords on each user account will mitigate this risk.
How To Do It
- A combination of lower and uppercase letters, along with numerals and symbols, should be used.
- For high security, consider a password management system that can generate and store complex passwords.
- In order to ensure safety over a period of time, passwords should be changed regularly.
3. Limit Login Attempts
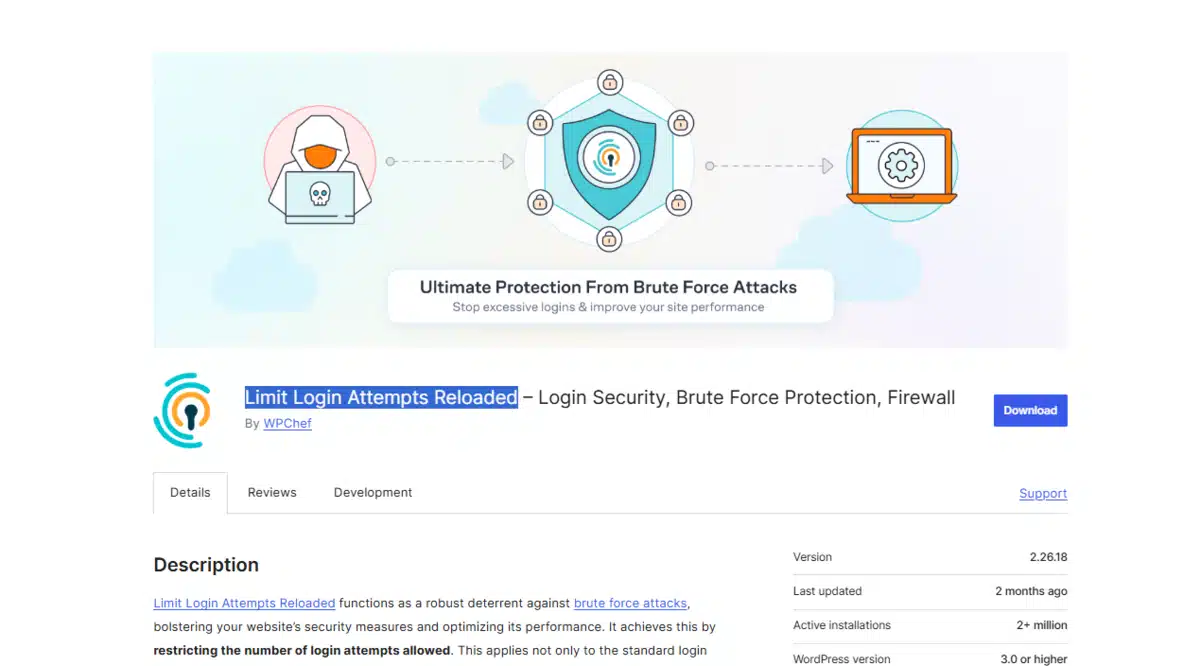
Why It Matters
Attackers often use automated bots to try a large number of password combinations. Limiting login attempts is one of the main methods of our WordPress security checklist that can mitigate the risk of brute force attacks by locking out users after a predefined number of failures.
How To Do It
- Install a plugin like Limit Login Attempts Reloaded.
- Configure IP blocking for repeated failed attempts.
- Monitor your login logs to identify suspicious behaviour.
4. Install a Reputable Security Plugin

Why It Matters
A comprehensive security plugin can offer a suite of protections from malware scanning to firewall rules—under one roof. It simplifies the process of maintaining a secure WordPress environment.
How To Do It
- Choose well-reviewed security plugins such as Wordfence Security, Sucuri Security, or iThemes Security.
- Regularly update the plugin and review its settings.
- Customize the security features to suit the needs of your website.
5. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Why It Matters:
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring a secondary verification method. This method of our WordPress security checklist ensures that even if your password is compromised, an unauthorized user would still need a second factor, like a code sent to your mobile device, to gain access.
How To Do It:
- Use plugins like Google Authenticator or Duo Two-Factor Authentication.
- Set up 2FA for all administrative accounts and encourage your users to activate it.
- Regularly check 2FA configurations and update your authentication methods if needed.
6. Change the Default “Admin” Username
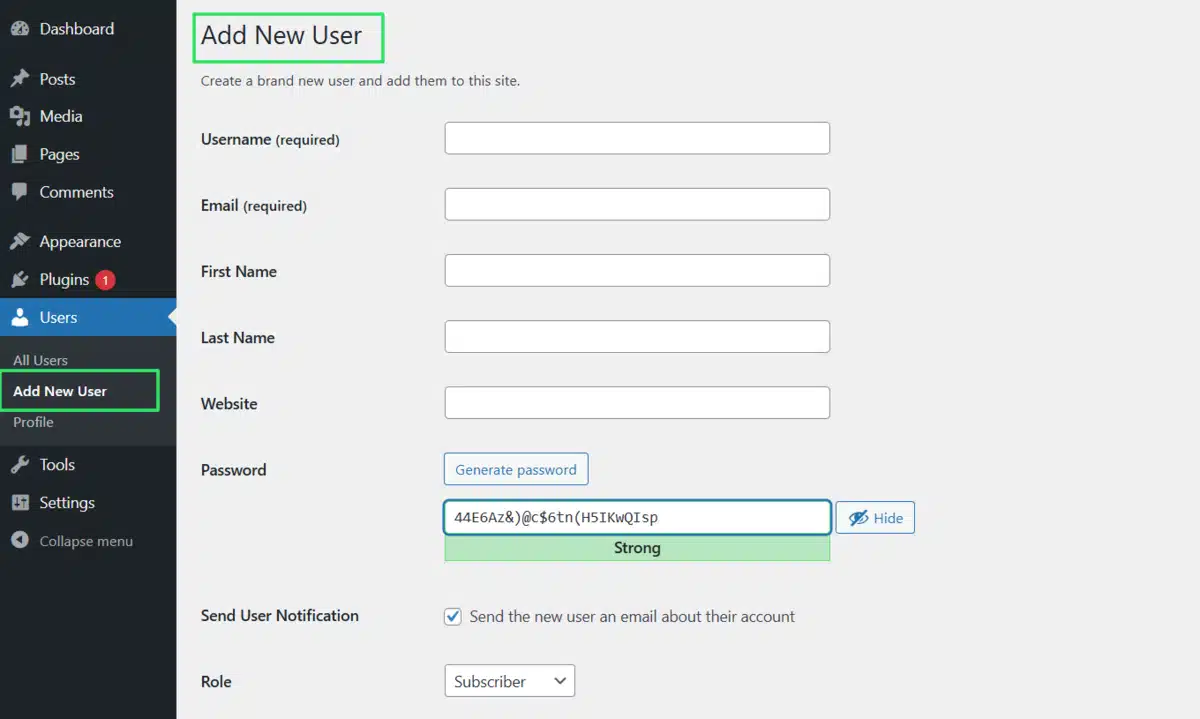
Why It Matters
Using the default “admin” username makes it easier for attackers to guess your login credentials. Changing this username complicates brute force attempts, as it adds an extra step for the attacker.
How To Do It
- Create a new administrative account with a unique username.
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Users > Add New.
- Fill in a new username (not “admin”), set a strong password, and assign the Administrator role.
- Click Add New User.
- Delete or downgrade the default “admin” user.
- Ensure that the new username is hard to guess and not associated with personal information.
7. Use the Latest PHP Version
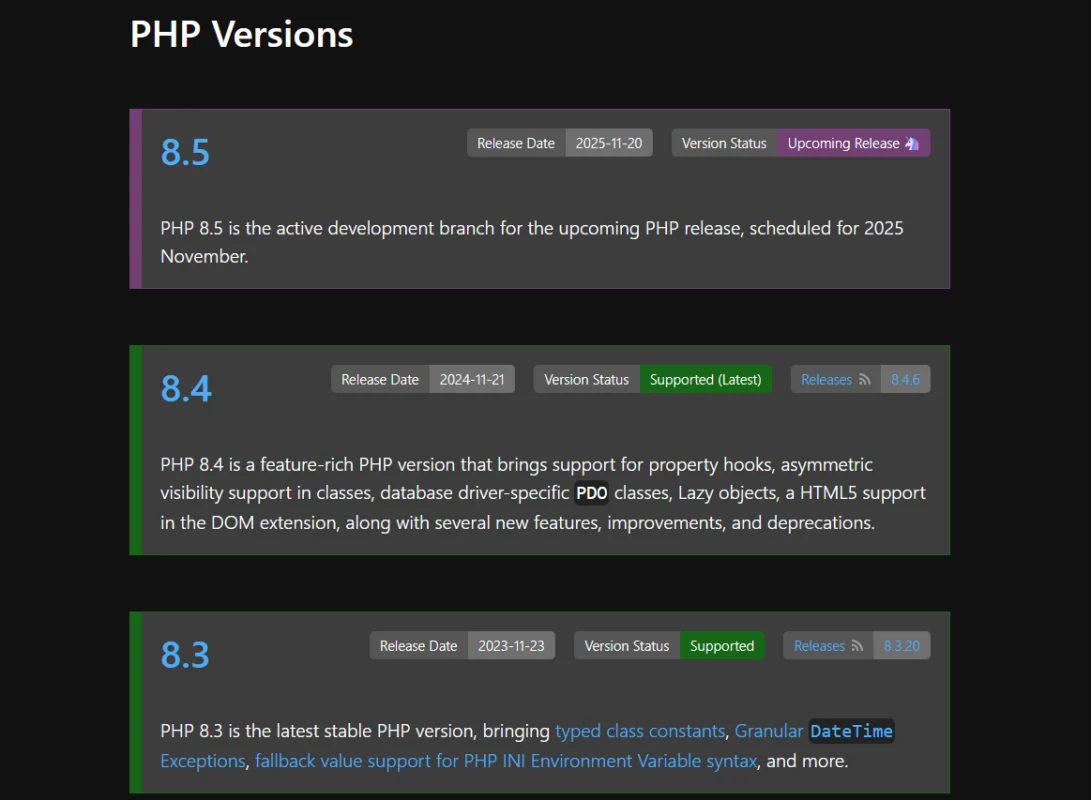
Why It Matters
Using an outdated PHP version can expose your website to known vulnerabilities. Newer PHP versions offer improved security features and performance enhancements, making them a better choice for hosting your WordPress website.
How To Do It
- Check your hosting provider’s PHP version settings and upgrade if necessary.
- Test your website on a staging environment after upgrading to avoid WordPress security issues.
- Monitor PHP updates and apply them promptly.
8. Secure the wp-config.php File
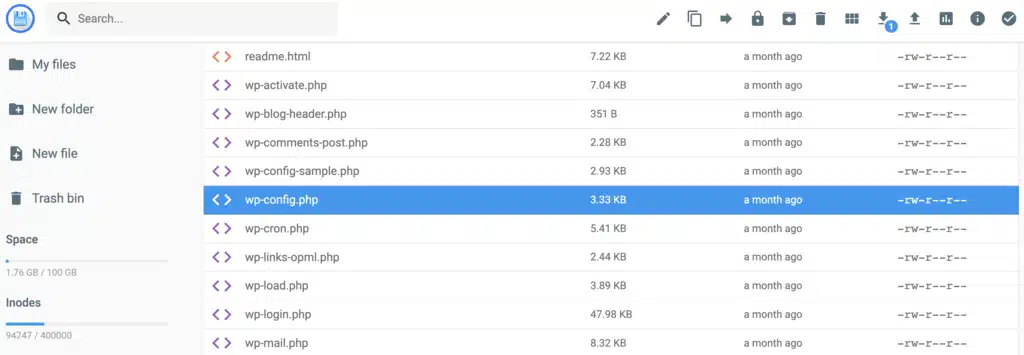
Why It Matters
The wp-config.php file contains sensitive configuration settings and database credentials. If exposed, it can be a goldmine for attackers looking to compromise your website.
How To Do It
- Move the wp-config.php file to a non-public directory if your host allows it.
- Restrict file permissions so that only necessary users can access it (typically set to 400 or 440).
- Consider adding rules in your .htaccess file to block unauthorized access to wp-config.php.
9. Use HTTPS With an SSL Certificate
Why It Matters
HTTPS encrypts data between your user’s browser and your website server, safeguarding sensitive information from interception. An SSL certificate not only boosts security but also builds trust with visitors and has a positive impact on SEO.
How To Do It
- Obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted provider (many hosts offer free certificates via Let’s Encrypt).
- Update your WordPress settings and site URLs to use HTTPS.
- Use plugins like Really Simple SSL to manage the transition seamlessly.
10. Disable File Editing in the Dashboard
Why It Matters
Allowing file editing from the WordPress dashboard can be risky if hackers gain access to your admin panel. Disabling this feature reduces the risk of arbitrary code execution; hence, it becomes one of the essential methods in our WordPress security checklist.
How To Do It:
- Open wp-config.php (in your main WordPress folder).
- Paste this line above the line that says, “That’s all, stop editing!”:
define( 'DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true ); - Save the file.
11. Regular Backups
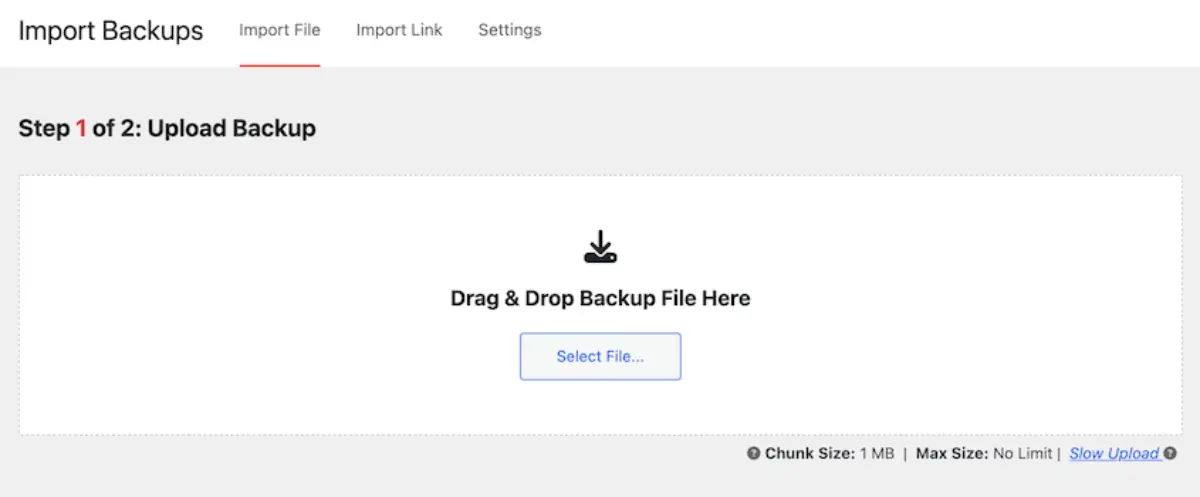
Why It Matters
Even with robust security measures, breaches can still occur. Regular backups ensure you can restore your website quickly with minimal downtime and data loss.
How To Do It
- Use backup plugins like UpdraftPlus, BackupBuddy, or VaultPress.
- Schedule automatic backups and store them in multiple locations (cloud storage and local backups).
- Test restore procedures periodically to ensure backup integrity.
12. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
Why It Matters
A Web Application Firewall adds an extra barrier between your website and potential threats. It monitors and filters incoming traffic, blocking malicious requests before they reach your site.
How To Do It
- Choose between a plugin-based WAF (e.g., Wordfence) or a cloud-based solution (e.g., Cloudflare, Sucuri).
- Configure the firewall settings based on the threats most likely to affect your website.
- Combine WAF with intrusion detection systems for layered security.
13. Set Correct File Permissions
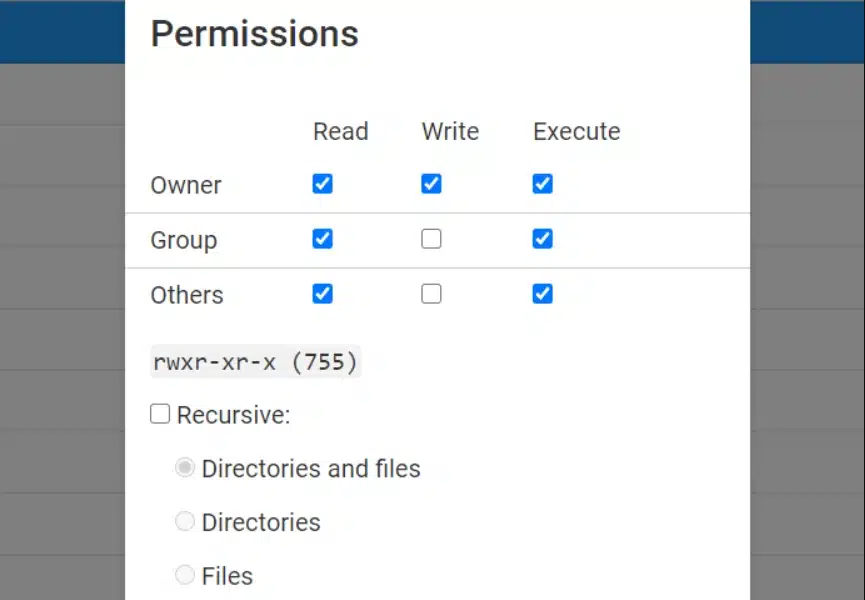
Why It Matters
Improper file permissions can leave your WordPress installation vulnerable to unauthorized changes. Setting correct permissions protects both files and folders from malicious access.
How To Do It
- For folders, set permissions to 755, and for files, use 644.
- Use secure FTP practices and avoid using root credentials where possible.
- Regularly review and adjust file and folder permissions using your hosting control panel.
14. Hide WordPress Version
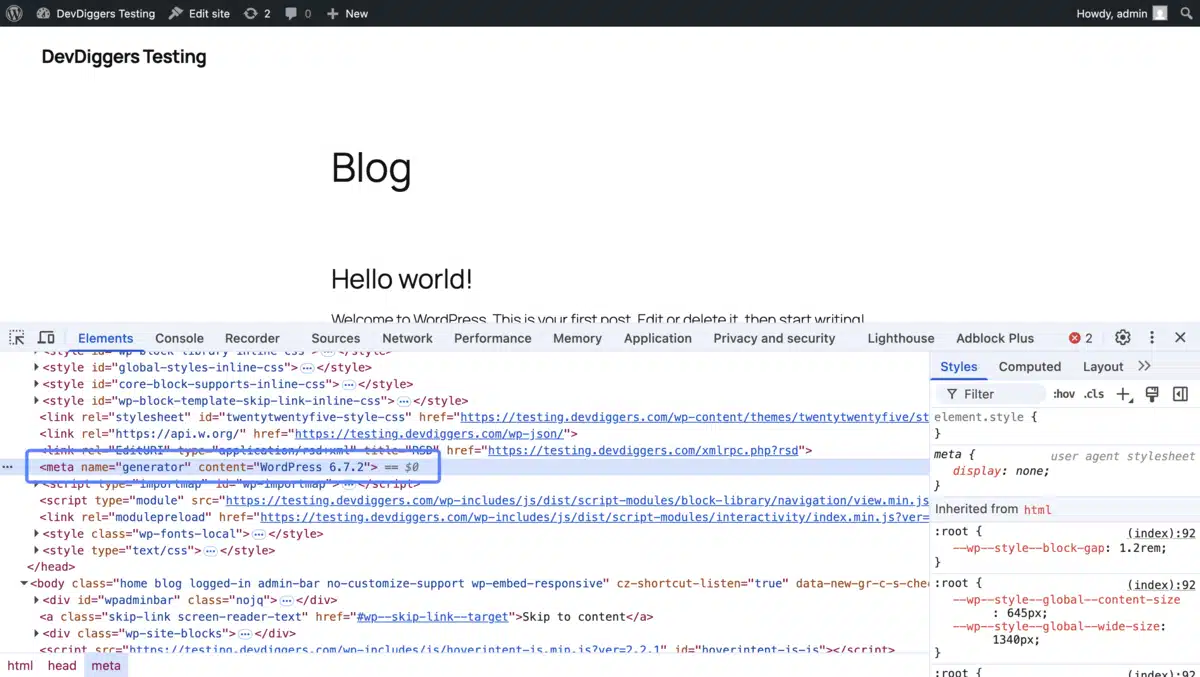
Why It Matters
Exposing your WordPress version makes it easier for attackers to identify vulnerabilities specific to that version. Hiding this information is a simple yet effective way to improve security.
How To Do It
- Remove the version number from your site’s header and meta tags.
- Use a security plugin that hides version information.
- Regularly update WordPress; this minimizes the risk of common exploits associated with older versions.
15. Implement Security Headers
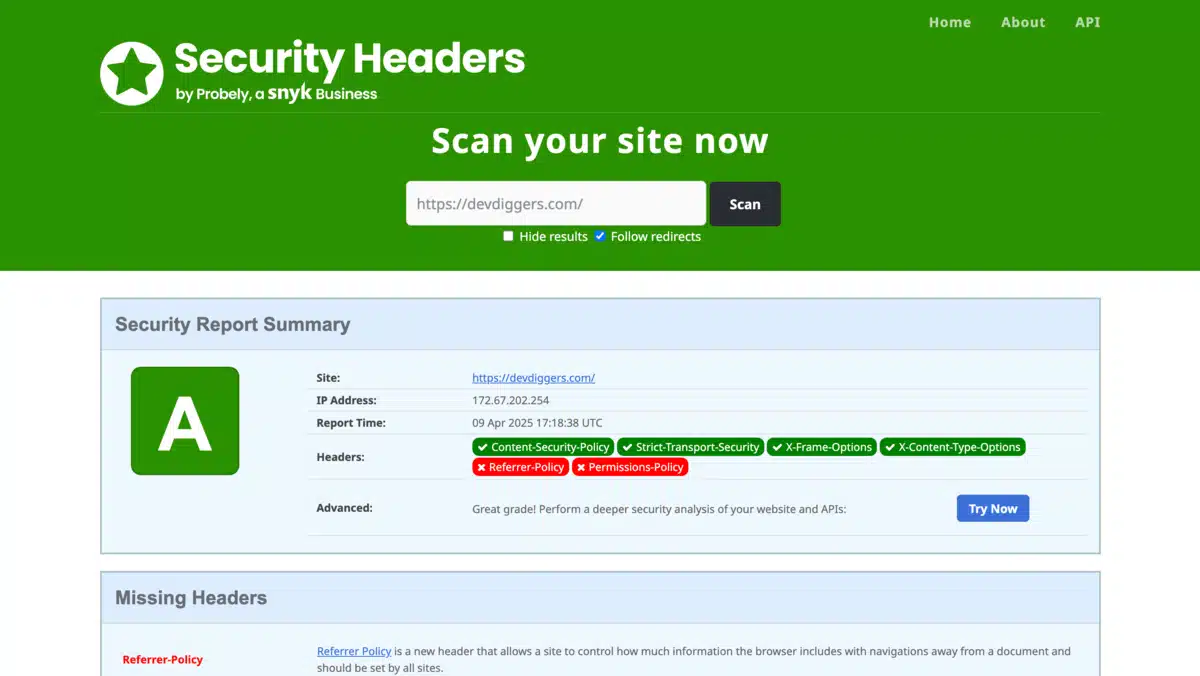
Why It Matters
Security headers are an important component of our WordPress security checklist as they add another layer of protection by instructing web browsers on how to handle your site’s content securely. These headers can protect against a range of attacks, including cross-site scripting (XSS) and clickjacking.
How To Do It
- Add headers like Content-Security-Policy, X-Frame-Options, X-XSS-Protection, and Strict-Transport-Security to your .htaccess or server configuration files.
- Use online tools to verify your headers are working as intended.
- Regularly audit these settings as part of your security best practices.
16. Remove Unused Themes and Plugins
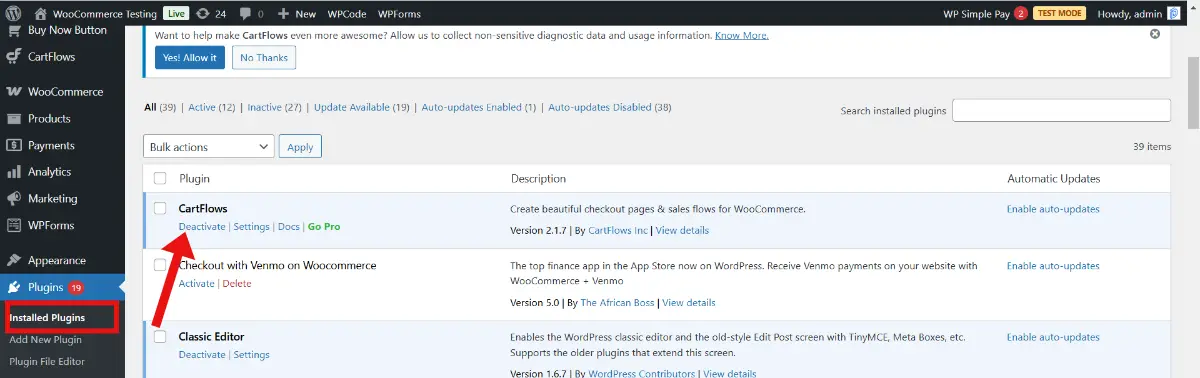
Why It Matters
Unused or outdated themes and plugins can harbour vulnerabilities and become entry points for hackers. Regularly cleaning up your WordPress installation minimizes these risks.
How To Do It
- Deactivate and remove any themes or plugins that aren’t in use.
- Regularly review your installed components for WordPress security updates.
- Only install plugins from reputable sources and check their ratings and reviews before use.
17. Monitor and Audit Logs
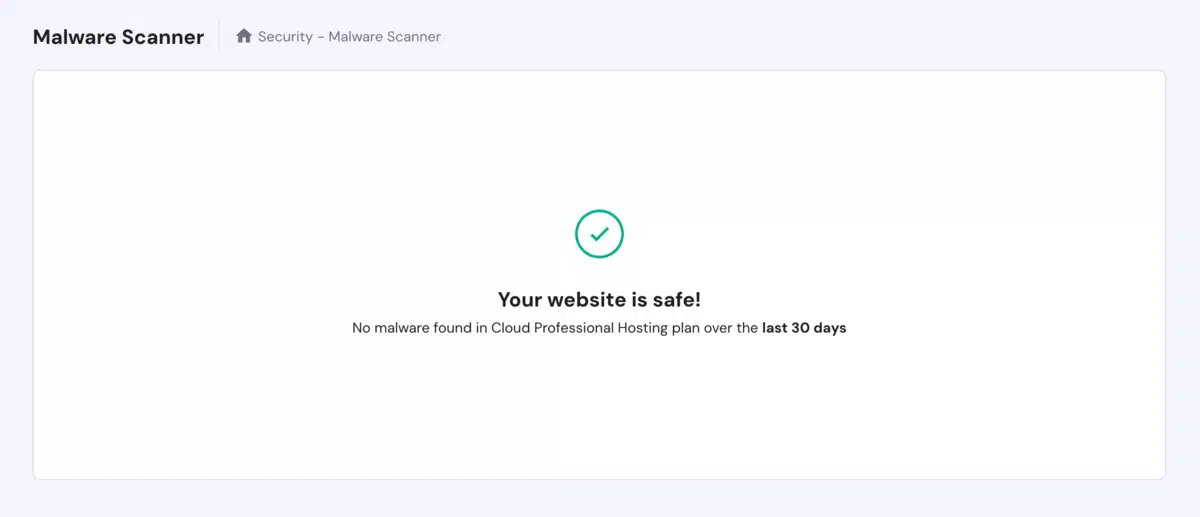
Why It Matters
Keeping an eye on your website’s activity logs enables you to detect suspicious behaviour early. Monitoring logs can reveal brute force attacks, unauthorized logins, or file modifications.
How To Do It
- Use the best WordPress security plugins that offer logging features (e.g., Sucuri, Wordfence).
- Regularly review activity logs for anomalies.
- Set up alerts to notify you of significant changes or repeated failed login attempts.
18. Harden Your Database
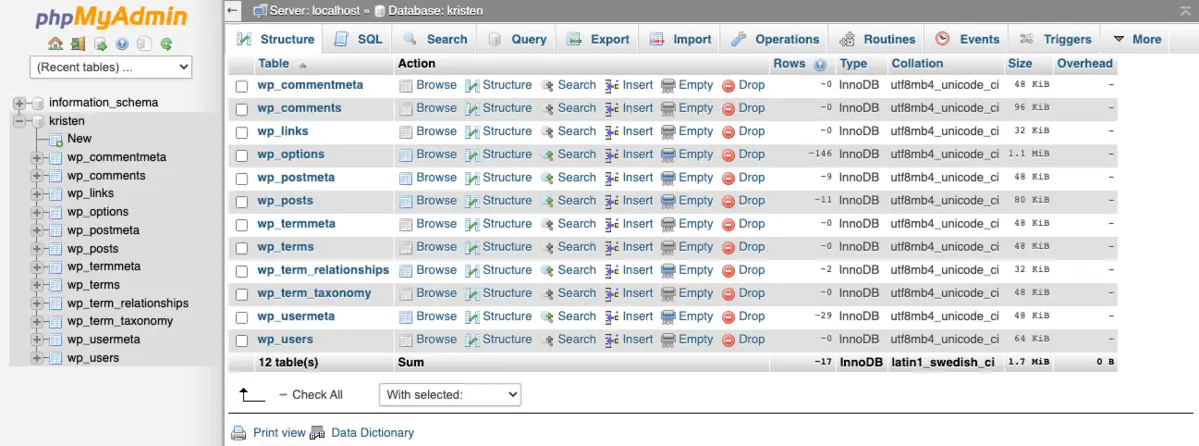
Why It Matters
The WordPress database is the heart of your website. Hardening it prevents SQL injections and unauthorized data access, ensuring that your data remains secure even if an attacker breaches the website front end.
How To Do It
- Change the default WordPress table prefix (from
wp_to something unique) during installation or via a plugin. - Restrict database user permissions to only what is necessary.
- Regularly back up your database and use tools like phpMyAdmin with secure access controls.
19. Defend Against Bots and Spam
Why It Matters
Bots can cause various problems—from overwhelming your server with requests to spamming your comment sections. Effective bot management protects your website’s performance and reduces unnecessary security risks.
How To Do It
- Use plugins like Akismet to filter out comment spam.
- Configure your site’s firewall to block known malicious bots.
- Implement CAPTCHA on forms to reduce automated submissions.
20. Implement Brute Force Prevention
Why It Matters
Brute force attacks involve repeated login attempts to crack your credentials. Implementing dedicated brute force prevention measures stops these attempts in their tracks.
How To Do It
- Employ plugins that limit login attempts and lock accounts after a set number of failures.
- Configure your .htaccess file or server rules to block IPs exhibiting suspicious behaviour.
- Combine these methods with strong password policies to reinforce overall security.
21. Restrict Access to wp-admin
Why It Matters
Limiting access to the WordPress admin dashboard reduces the number of potential points of attack. Only authorized IP addresses or users should have permission to access sensitive backend areas.
How To Do It
- Use IP whitelisting to restrict access to wp-admin and wp-login.php.
- Add additional password protection at the server level (using .htpasswd).
- Regularly update allowed IP addresses and monitor administrative access logs.
22. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) With Security Features
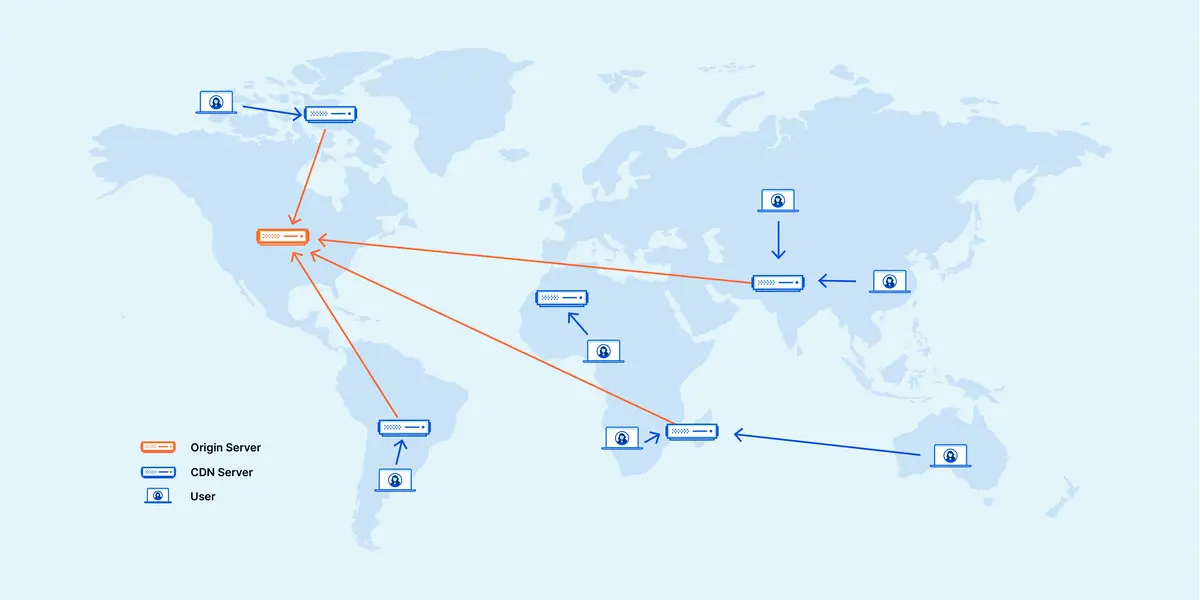
Why It Matters
A CDN not only speeds up your website by caching content across multiple servers worldwide but also provides security measures such as DDoS protection and threat mitigation. By distributing the load and intercepting malicious traffic, a CDN can serve as an additional shield.
How To Do It
- Choose a CDN provider that offers integrated security features (such as Cloudflare or Sucuri).
- Configure the CDN’s firewall and caching settings to complement your existing security layers.
- Monitor CDN performance and security logs regularly to adapt to evolving threats.
23. Disable PHP File Execution in Untrusted Directories
Why It Matters
Hackers often upload malicious PHP files in directories like /wp-content/uploads. Disabling execution in such folders stops those files from running even if uploaded.
How To Do It
Step 1: Go to Your Hosting Panel
- Log in to your web hosting account (like Hostinger, Bluehost, etc.).
- Open File Manager from your dashboard.
Step 2: Find the Uploads Folder
- Navigate to:
- public_html > wp-content > uploads
Step 3: Create a New File
- Click New File or Create File.
- Name it exactly: .htaccess
Step 4: Paste This Code Inside:
<Files *.php> deny from all </Files>
Step 5: Save the File
That’s it! You’ve blocked PHP files from running in that folder.
24. Disable Directory Indexing and Browsing
Why It Matters
Directory browsing allows visitors (and potential hackers) to see the contents of your website folders if there’s no index file present. This can expose sensitive files, plugin details, or themes that help attackers plan targeted exploits.
How To Do It
- Open your website’s root .htaccess file (typically found in public_html).
- Add this line at the bottom:
Options -Indexes - Save and upload the file back to the server.
Bonus Tip: Test by visiting a directory URL like yoursite.com/wp-content/uploads/. If configured correctly, it should show a 403 Forbidden or redirect instead of listing files.
25. Set Up Automatic Logouts for Idle Users
Why It Matters
Idle sessions—especially from admin accounts—are an open invitation to attackers, especially on shared or public devices. Auto-logout ensures that inactive users are logged out, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
How To Do It
- Use plugins like Inactive Logout or Idle User Logout.
- Set a timeout limit (e.g., 15 minutes) for inactivity.
- Customize logout warnings or redirect users to the login page upon timeout.
Best Practice: Combine this with 2FA for a rock-solid session security setup.
Final Thoughts on our WordPress Security Checklist
To protect your WordPress site, simply adding the best WordPress security plugin won’t do the job. You need to build a more security-oriented way of thinking and implement a multi-layered approach.
These 25 ways of our WordPress security checklist serve as a comprehensive guide to protect your website, ranging from the more simplistic tasks like routinely updating WordPress and setting strong passwords to more advanced techniques, including two-factor authentication, the use of security headers, and utilizing more secure CDNs.
Every step taken in securing your WordPress site adds to the security framework that makes your website more secure from security breaches, preserves sensitive data, and maintains the integrity of the website.
It is crucial to understand that the entire security system is an ongoing project that requires constant surveillance, timely updates, and active intervention for added protection.
Frequently Asked Questions: How to Improve WordPress Security
Q1. Why is WordPress security update an important matter?
Routine updates close security gaps, minimizing the chance of hackers taking advantage.
Q2. How does enabling two-step verification improve login security?
Security is improved by requiring more than just one check for permission.
Q3. What is meant by a brute force attack?
This is trying to gain access by using a methodical approach to log in with different passwords.
Q4. Why should unused plugins be deleted?
Inactive plugins get outdated and pose a potential security threat.
Q5. How do strong passwords protect my site?
Strong passwords protect a site by making it difficult to guess or crack logins.

Abhijit Sarkar
Hi, I’m Abhijit Sarkar. I am deeply passionate about creating engaging content and exploring. My journey includes gaining valuable experience in content writing and creating useful resources for my readers.

Leave a Reply